Last Updated on October 23, 2025
We often talk about helping Google understand our content. Schema markup is one of the best ways to do this.
Think of a website’s content as a recipe. A search engine can read the text and see “flour,” “sugar,” and “butter,” but it doesn’t know what each ingredient is or how they relate to each other. Structured data is like adding a nutrition label and clear instructions to the recipe. It uses a specific format to explicitly tell search engines what your content is about—whether it’s an article, a product, a local business, or an event—and to highlight key details like ratings, prices, or locations.
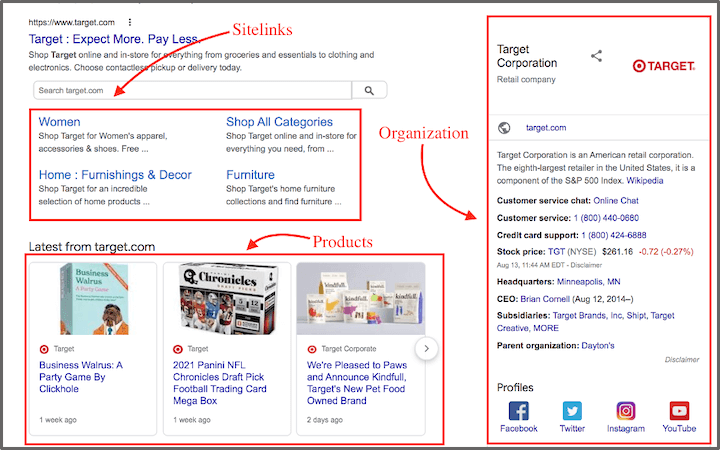
One of the main benefits to putting schema in place is that they make it more likely that you’ll qualify for “rich results” (or “rich snippets”). Rich results are kind of like Google Ads assets (extensions) for organic results. They can display your content in more visually appealing and informative ways. Some examples are:
- Organic sitelinks
- Star ratings for products/reviews
- Event info (time, location)
- FAQs
Similar to Google Ads assets, rich results can significantly improve your click-through rate (CTR).
Most Useful Schema Types for Digital Marketing
There are tons of schema types, but a few are particularly valuable for our purposes: Article, Product, Review, FAQ, LocalBusiness, and Organization.
This is a foundational schema for any website. It is set at the website-level (not specific page-types) and provides information about a company, such as its name, official logo, contact information, and social media profiles.
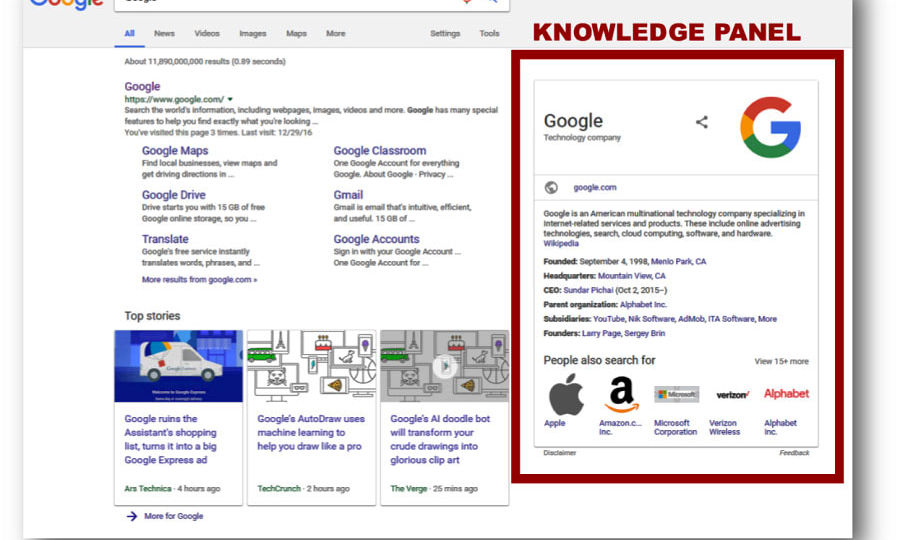
Essential for any client with a physical location. This schema provides details like the address, phone number, opening hours, and a map location, helping the business appear in local search results and the Google Knowledge Panel.
Google Knowledge Panel:
Use on blogs, news sites, and any other content-driven website. It helps search engines understand the title, author, publish date, and main content of an article, which can lead to better visibility and placement in Google News or Top Stories. For Sebo, this will be one of the most commonly used Schemas (since most of our clients have blogs).
Rich result example:

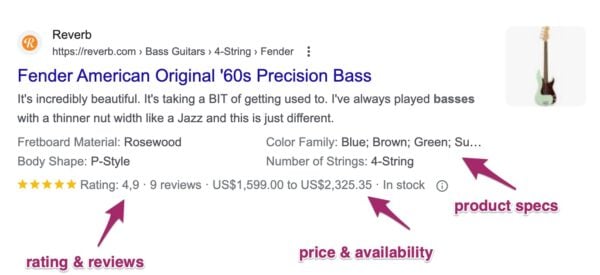
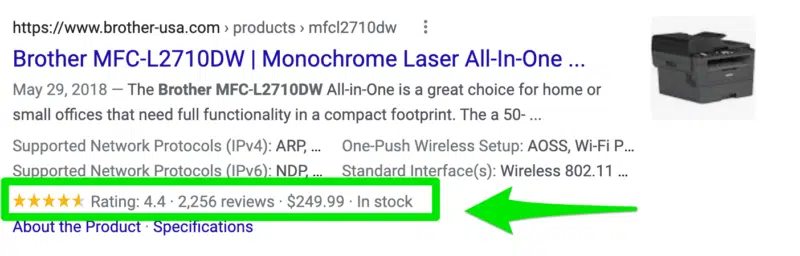
Crucial for e-commerce clients. This markup highlights key product information like price, availability, and customer ratings, which can display as star ratings and other rich results directly in Google Search.
Rich results example:
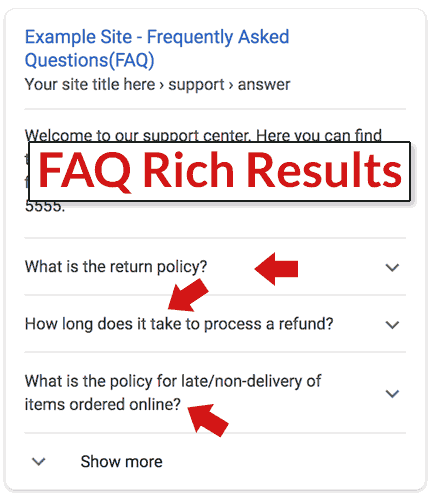
Should be used on any FAQ page. This schema can enable Google to display the Q&A content as a collapsible rich result on the SERP.
Rich result example:
This is used to mark up reviews and ratings for a product, business, or service.
Example:
How to Implement Schema Markup
For most modern websites, there are two primary ways to implement schema. How you implement schema will vary based on your situation:
Schema Pro: We have an unlimited-use license for a plugin called “Schema Pro”. This plugin should cover all of our schema needs for WordPress sites. Here are directions for getting it onto a client’s site:
- Navigate to https://wpschema.com/.
- Log in as agency@sebomarketing.com.
- Put in the confirmation code (sent to the agency@sebomarketing.com email).
- Click the “download” icon next to “SCHEMA PRO”.
- Log into the backend of the client’s site.
- Click “Plugins” -> “Add Plugin” -> “Upload Plugin”
- Drag the Schema Pro file you downloaded onto the “Choose File” box
- Click “Activate Plugin”
Unless a plugin or app is available, you will need to implement schema manually (you can also use manual, implementation on WordPress, it will just take longer). To do this, you will need to place static code on each applicable page (except for schema that applies site-wide, like “organization” schema. That can be implemented site-wide).
Generating Schema
- ChatGPT
- Definitely the quickest way to generate your schema. For example, you can give ChatGPT the URLs of all of your location pages and ask it to generate localBusiness schema for each page. You may need to spot check it a little bit (it often messes up the “Name” part), but it mostly works really well.
- Structured Data Markup Helper
- A Google tool that helps you generate your own schema. You plug in a URL, and then highlight and tag each item. Then, you export the html, copy it, and then paste it into your page/site.
Once you have your html copied, you need to get it onto the page. You can do that by:
- Pasting it straight onto the page (using an html/code block)
- Using a GTM “Custom HTML” tag
- Paste your html into the tag, set the trigger to “page view”, and then set the condition “Page URL = *Insert page URL*.
- For schema that applies site-wide, simply change the trigger to “all pages”.
- Paste your html into the tag, set the trigger to “page view”, and then set the condition “Page URL = *Insert page URL*.
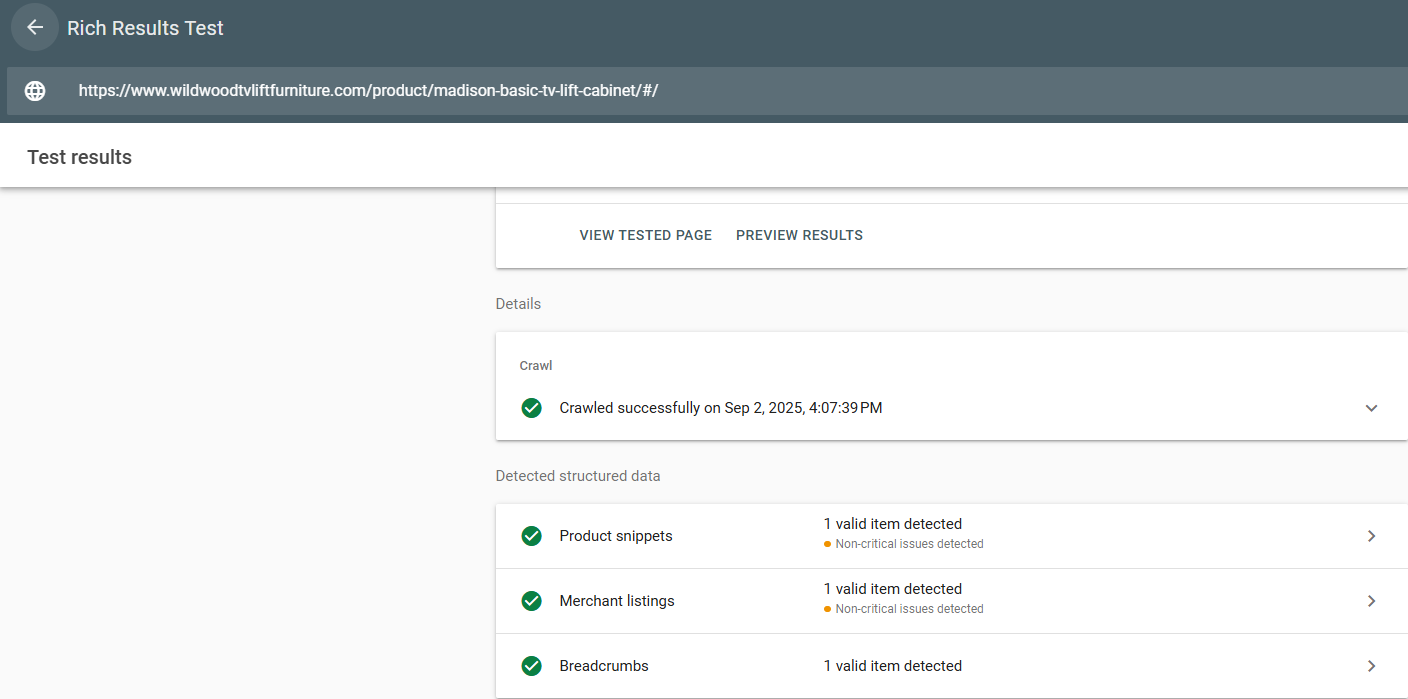
How to Make Sure Your Schema Is Working
Making sure your schema is working is a pretty simple process. All you need to do is:
- Go to the Google Rich Results tool.
- Enter the URL you are testing.
- Verify that your desired rich results are showing up.
For example, in the picture on the right, we tested a Wildwood TV Lift Furniture product page. We are hoping to AT LEAST see “product” schema in place. It looks like they have a few more things going on in addition to “product” schema, but they do have the correct schema in place.
If you don’t see the schema that you are expecting, you may need to troubleshoot further.